Nov . 11, 2024 14:27 Back to list
quizlet phys 1040 refractory materials
Understanding Refractory Materials in Physics
Refractory materials play a crucial role in various engineering and industrial processes, particularly in environments that encounter extreme temperatures. These materials are designed to withstand high heat without deforming or losing their structural integrity, making them essential in industries such as steel, glass, cement, and ceramics. This article aims to explore the properties, applications, and significance of refractory materials in the field of physics.
Properties of Refractory Materials
Refractory materials are defined by their exceptional ability to endure high temperatures—typically above 1,500°C (2,732°F)—and their resistance to thermal shock. These materials possess several key properties
1. High Melting Points Refractories are characterized by their high fusion temperatures, which prevent them from melting or softening when exposed to extreme heat.
2. Thermal Conductivity They generally exhibit low thermal conductivity, which helps in conserving energy and maintaining temperature stability within furnaces and kilns.
3. Chemical Stability Refractories are resistant to chemical corrosion from slag, molten metals, and other aggressive substances, preserving their structural integrity over time.
4. Mechanical Strength High tensile and compressive strength at elevated temperatures ensures that refractory materials can support the loads and stresses they encounter in industrial applications.
5. Thermal Shock Resistance The ability to endure rapid changes in temperature without fracturing is critical for materials used in processes that involve quick heating and cooling cycles.
Types of Refractory Materials
Refractory materials can be categorized into two main types acidic and basic refractories.
- Acidic Refractories Made from silica (SiO2) and alumina (Al2O3), these materials are commonly used for lining furnaces that process acidic slags and materials, such as glass-making and certain steel production processes.
quizlet phys 1040 refractory materials
- Basic Refractories Composed mainly of basic oxides like magnesia (MgO) and lime (CaO), these refractories are suitable for environments where basic slags are predominant, such as in the production of basic steel.
In addition to these categories, there are also special refractories designed to meet specific needs, such as insulating refractories, which possess lower densities and thermal conductivities to improve energy efficiency.
Applications of Refractory Materials
The applications of refractory materials span a wide array of industries and processes.
1. Iron and Steel Industry Refractories are extensively used in blast furnaces, converters, and ladles, where they protect the furnace walls and support the processes of melting and casting.
2. Cement Production In cement kilns, refractories withstand the high temperatures required to convert limestone and other raw materials into clinker.
3. Glass Manufacturing Refractories are essential for lining glass melting furnaces, allowing for the high-temperature processes necessary to fuse silica and other raw materials.
4. Nuclear Applications Certain refractory materials are used in nuclear reactors due to their ability to tolerate high temperatures and their chemical stability against neutron irradiation.
5. Aerospace Refractories are utilized in thermal protection systems of spacecraft, protecting them from the extreme temperatures encountered during re-entry into the atmosphere.
Conclusion
Refractory materials are indispensable to modern industrial processes, offering unparalleled resistance to extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments. Their unique properties make them vital in sectors ranging from metallurgy to aerospace. Understanding the science behind these materials enhances our capability to design and utilize them effectively, leading to innovations that improve safety, efficiency, and productivity in high-temperature applications. As industries continue to evolve, the development of advanced refractory materials will undoubtedly play a key role in meeting future challenges.
-
High-Quality Fe-C Alloy Leading Manufacturers & Spherical Alloy Materials Supplier
NewsJun.10,2025
-
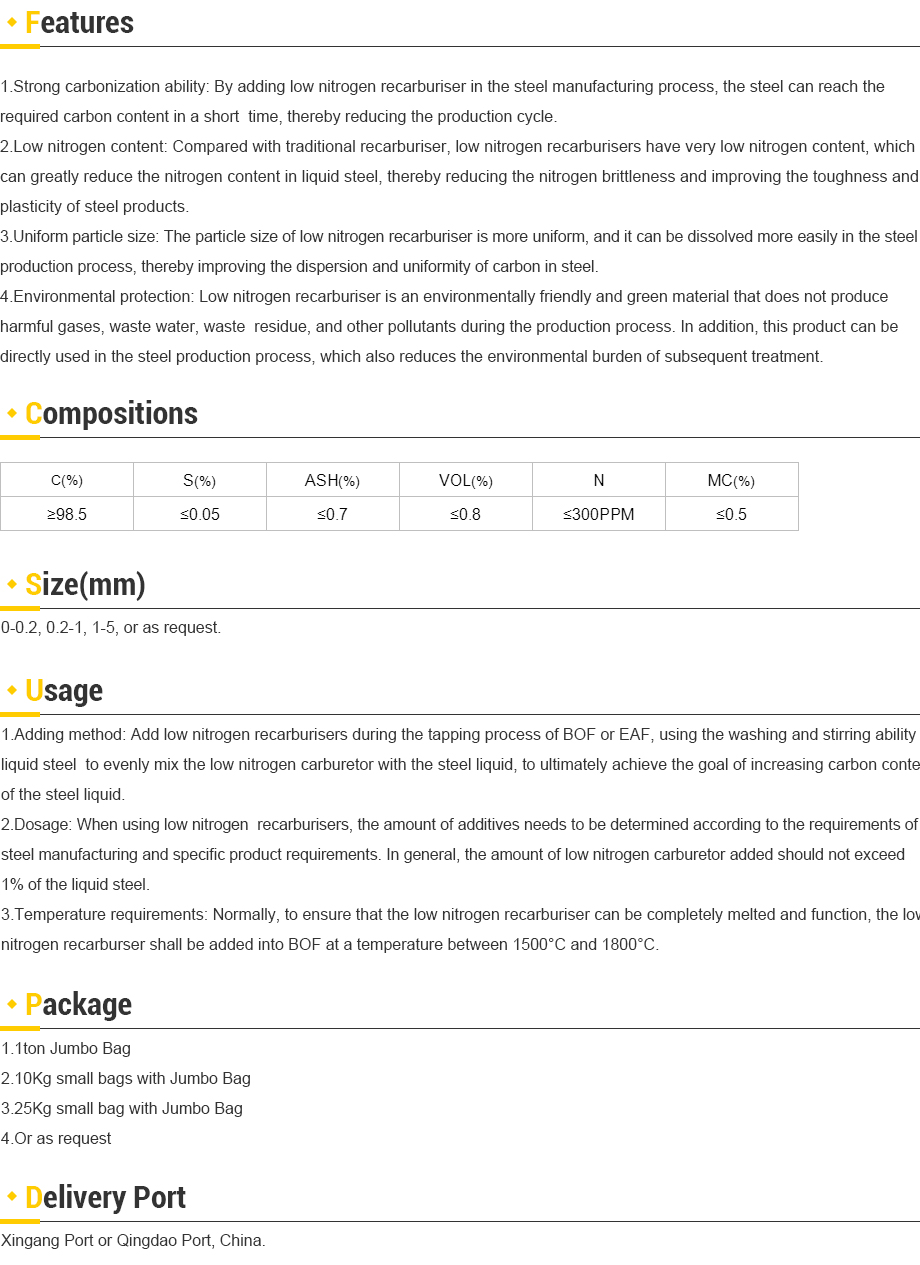
Premium Low Nitrogen Recarburiser Supplier & Manufacturer – High Quality Exporters
NewsJun.10,2025
-
DT4 High-Quality Magnetic Materials Leading DT4 Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High-Performance Spring Steel Suppliers Custom Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Premium SWRCH6A Manufacturer Steel Wire Supplier & Factory
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Premium Mild Steel Wire Rod Supplier & Manufacturer
NewsJun.10,2025
