Sep . 14, 2024 21:58 Back to list
thermal insulator thermal insulator materials
Understanding Thermal Insulators Materials and Applications
Thermal insulators are materials that significantly reduce the rate of heat transfer between two surfaces or environments. They play a crucial role in various industries, from construction to manufacturing, and are essential for energy conservation and thermal management in numerous applications. This article will explore the types of thermal insulator materials, their properties, and their applications in everyday life.
Thermal insulators work based on their ability to impede the flow of heat. When two bodies are at different temperatures, heat naturally flows from the hotter to the cooler body. Insulating materials slow down this process, maintaining temperature differences for prolonged periods. The effectiveness of an insulator is measured by its thermal conductivity—lower values indicate better insulating properties.
Common materials used as thermal insulators include fiberglass, foam, mineral wool, and certain plastics. Fiberglass, composed of fine glass fibers, is widely used in residential and commercial buildings. It is lightweight, resistant to moisture and rotting, and boasts a low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for insulation in walls, attics, and floors.
Foam insulators, such as polyurethane and polystyrene, offer excellent thermal performance, often used in refrigerator insulation as well as building applications. Polyurethane foam has exceptional insulating properties and can be sprayed directly onto surfaces to create a seamless barrier. Polystyrene foam, on the other hand, often comes in sheets and is frequently employed in roofing and foundation insulation.
thermal insulator thermal insulator materials
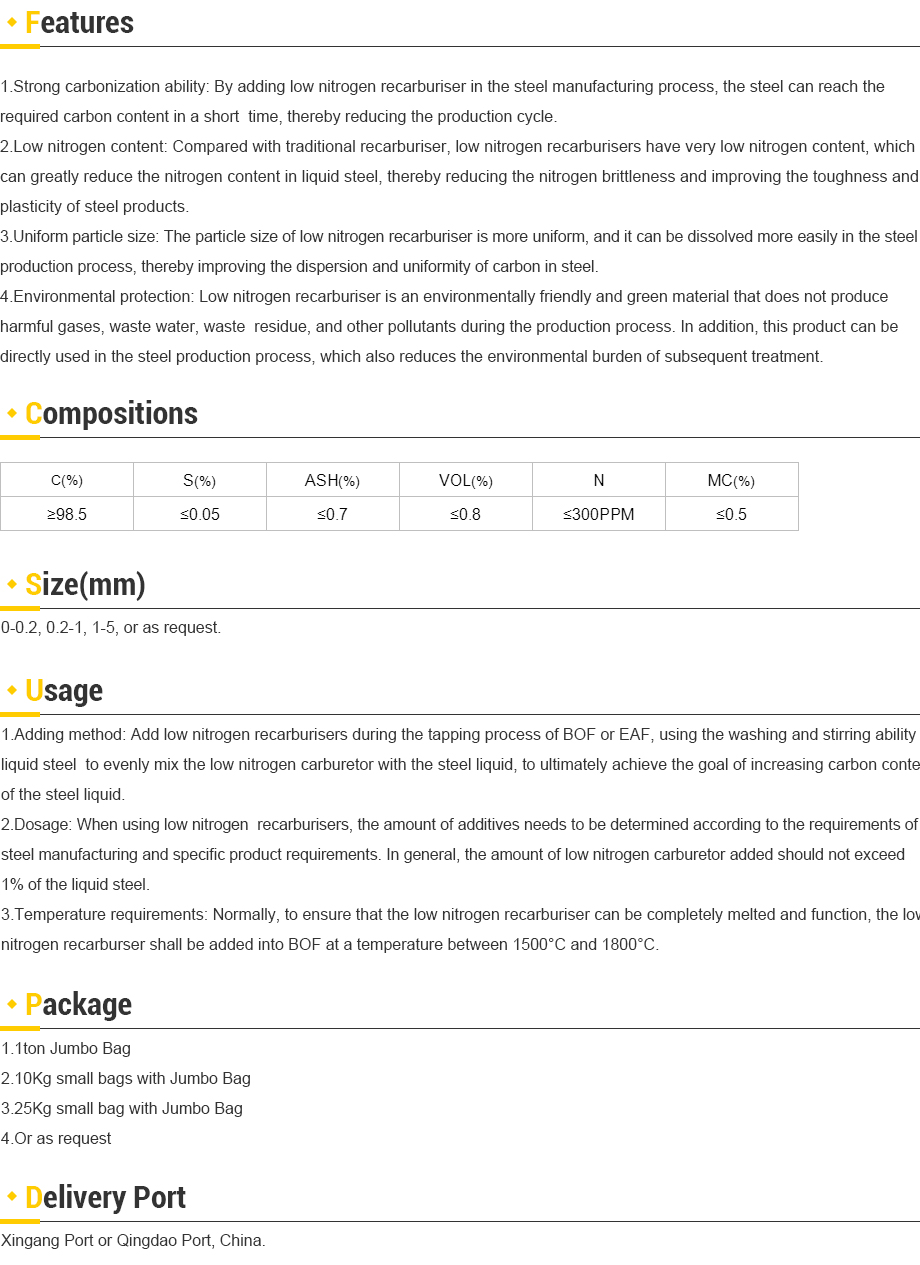
Mineral wool, another popular choice, is made from natural or synthetic fibers and is known for its fire-resistant properties. It is often used in commercial buildings and factories where fire safety is a critical concern. Moreover, mineral wool is also effective in soundproofing, providing dual benefits in certain applications.
When selecting an appropriate thermal insulator, it’s essential to consider various factors such as its environmental impact, cost, and specific application needs. Recent advancements in materials science have led to the development of eco-friendly insulation options made from recycled materials or renewable resources. These innovations help reduce the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing traditional insulating materials.
Thermal insulators find applications in a myriad of industries. In the construction sector, they help maintain comfortable indoor environments while reducing energy costs. In the automotive industry, thermal insulators are crucial for enhancing fuel efficiency and protecting occupants from extreme temperatures. Additionally, the aerospace sector uses advanced thermal insulation materials to protect sensitive equipment from extreme altitude temperatures.
In conclusion, thermal insulators are vital materials that enhance energy efficiency, comfort, and safety across various fields. With the ever-increasing emphasis on sustainability and energy conservation, ongoing research and development will likely yield even more efficient and environmentally friendly insulating solutions in the future. As industries adapt to these changing needs, the role of thermal insulators will continue to expand, underlying the importance of understanding their properties and applications for a more efficient world.
-
Eco-Friendly Granule Covering Agent | Dust & Caking Control
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Fe-C Composite Pellets for BOF: High-Efficiency & Cost-Saving
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Premium Tundish Covering Agents Exporters | High Purity
NewsAug.04,2025
-
Fe-C Composite Pellets for BOF | Efficient & Economical
NewsAug.03,2025
-
Top Tundish Covering Agent Exporters | Premium Quality Solutions
NewsAug.02,2025
-
First Bauxite Exporters | AI-Optimized Supply
NewsAug.01,2025
